iOS Simulator and Little Snitch 3.5
If you’re an iOS developer, this will make you very happy: Little Snitch 3.5 greatly improves support for iOS Simulator apps in every regard.
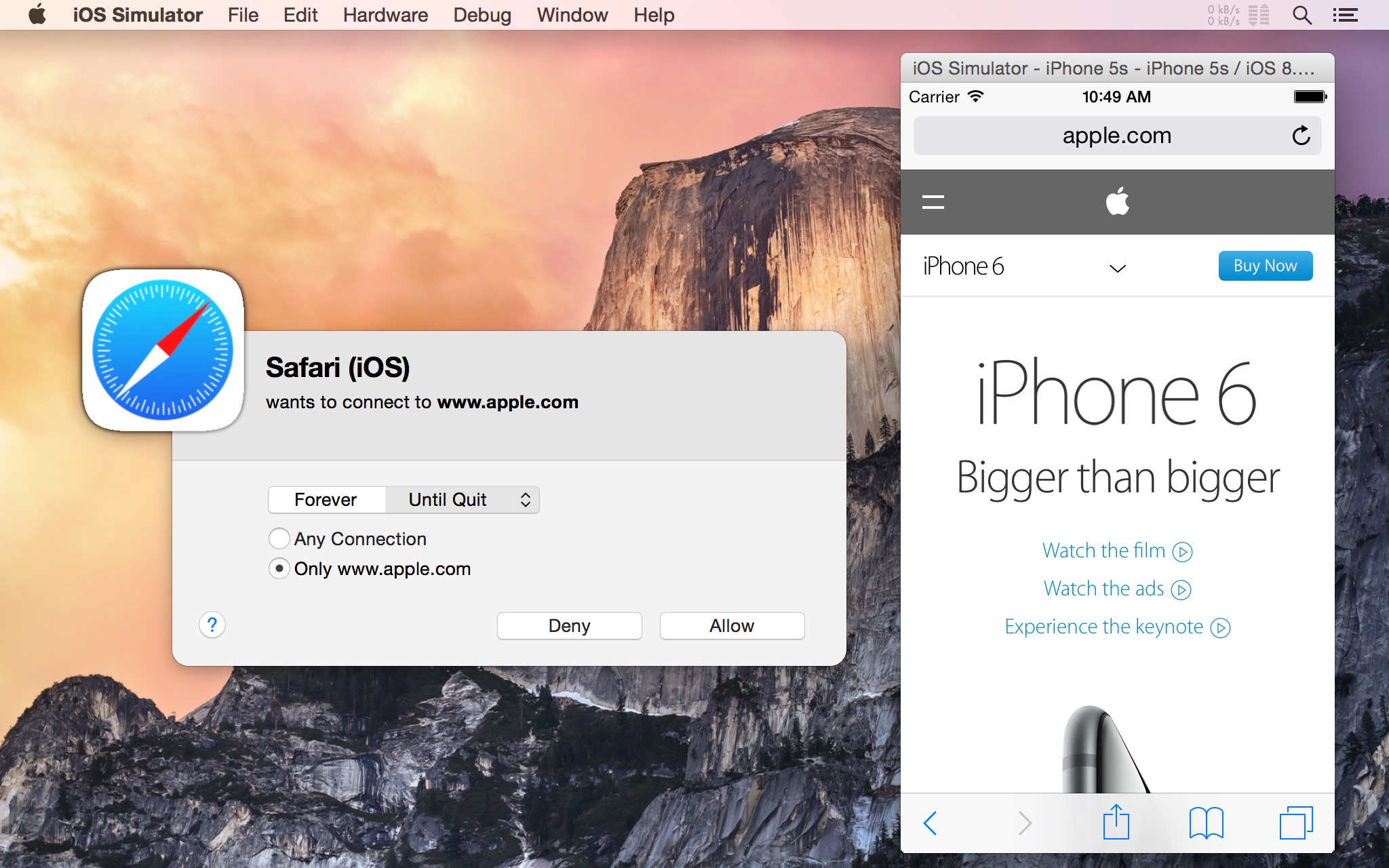
First and foremost, apps and processes that run in iOS Simulator are now easily recognizable by their name. For example, the iOS version of Safari is shown as “Safari (iOS)”:
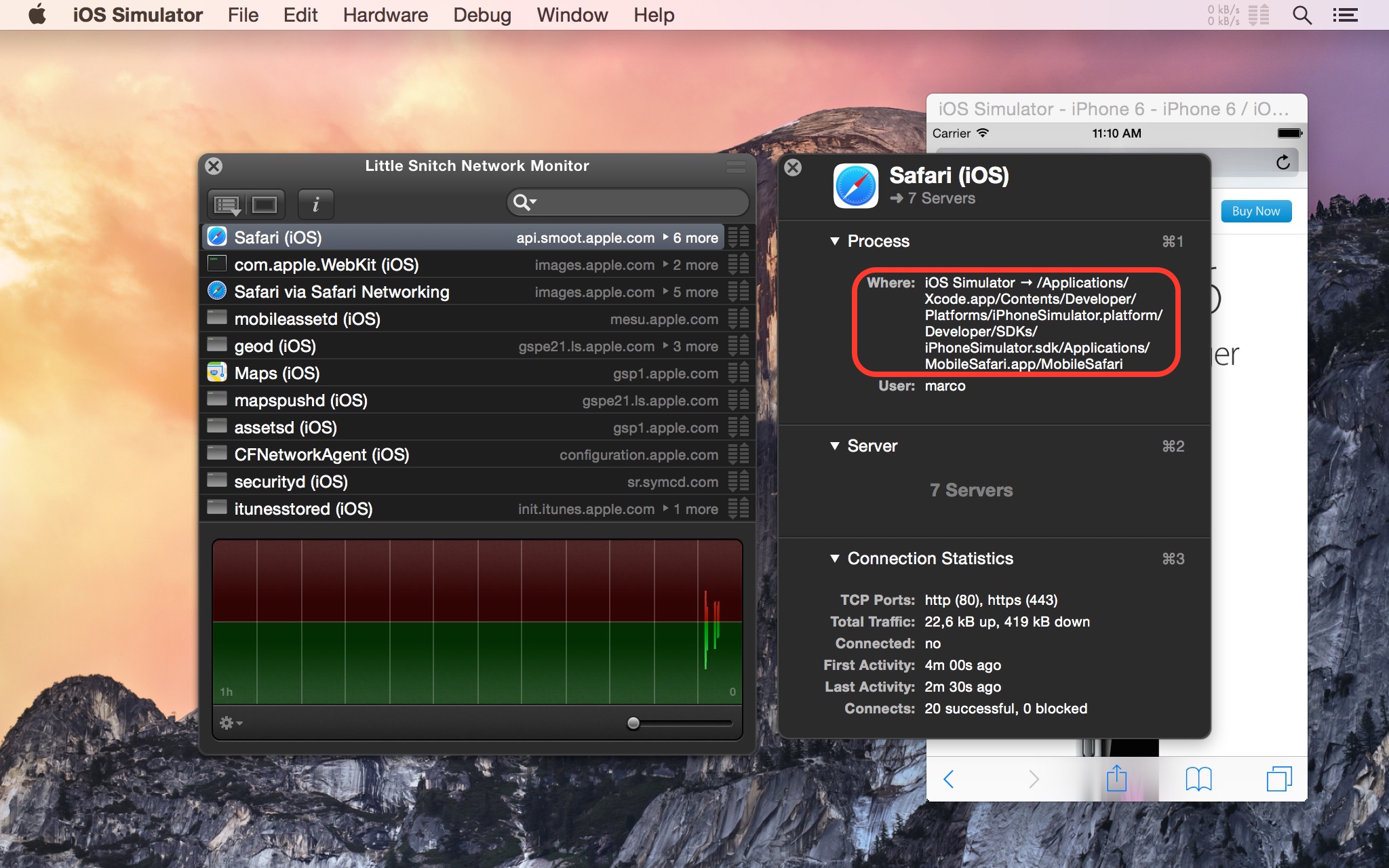
Paths to iOS Simulator apps are clearly marked with a prefix. For stock apps like Safari, Maps or an iOS system daemon, Little Snitch will show “iOS Simulator” followed by the full path to the app’s or process’ binary. That path will be somewhere deep inside the Xcode app bundle, as can be seen in the Network Monitor’s inspector:
Here comes the interesting part: What about apps that you as an iOS developer create and then test in iOS Simulator? If you ever poked around the file system and tried to find out how Xcode and iOS Simulator manage your apps on disk, you probably discovered a path that looks like this:
~/Library/Developer/CoreSimulator/Devices/97F0609B-D9D5-4B8B-A56E-170254F30F6B/data/Containers/Bundle/Application/A3CE365D-E348-439B-871A-A2884409831B/Test.app
Every app you test resides in a directory somewhere inside your home directory’s hidden Library folder whose name is a random unique identifier (UUID) that is generated for every combination of iOS version and iOS device flavor you test against which contains another random unique identifier and then your app. To top it all off, different versions of Xcode have different directory structures for all this (the above example is from Xcode 6).
In previous versions of Little Snitch all this caused problems because rules in Little Snitch are created for a process at a certain path. This means if you create a rule for an app, it only works as long as the path stays the same. Now, iOS Simulator apps don’t play nicely with this because every time Xcode and iOS Simulator decide to use a new path, you’d get a Connection Alert from Little Snitch when your app tried to do some networking.
Little Snitch 3.5 solves this problem by becoming aware of which apps on your Mac are actually run in iOS Simulator and whether they reside in one of iOS Simulator’s random container paths. For such apps, a rule’s path is automatically shortened to something like “iOS Simulator → Test.app/Test” and it just works regardless of what the exact path is.
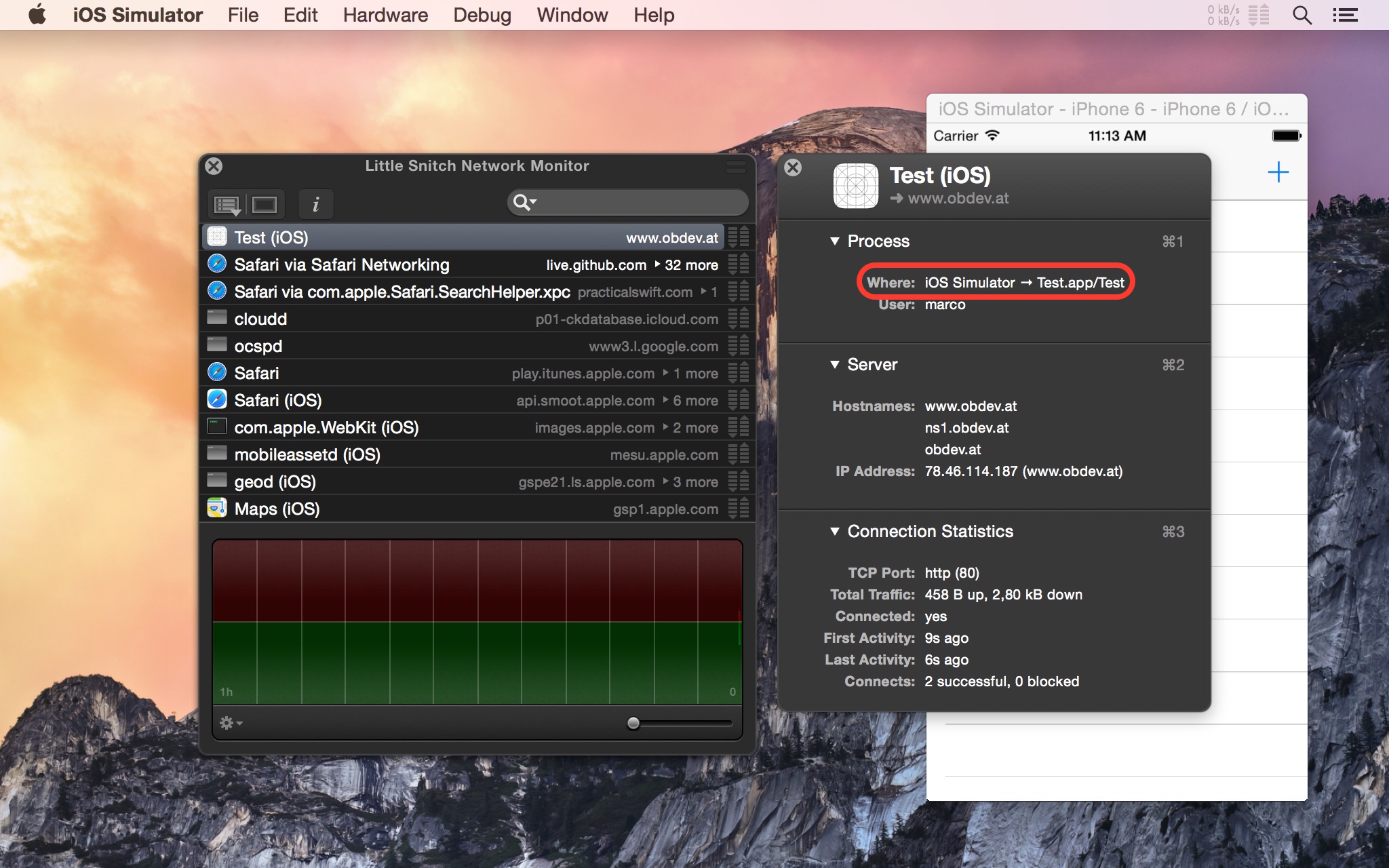
There’s nothing special you have to do as an iOS app developer. Rules can be created like any other rule using the Connection Alert, Network Monitor or Configuration.
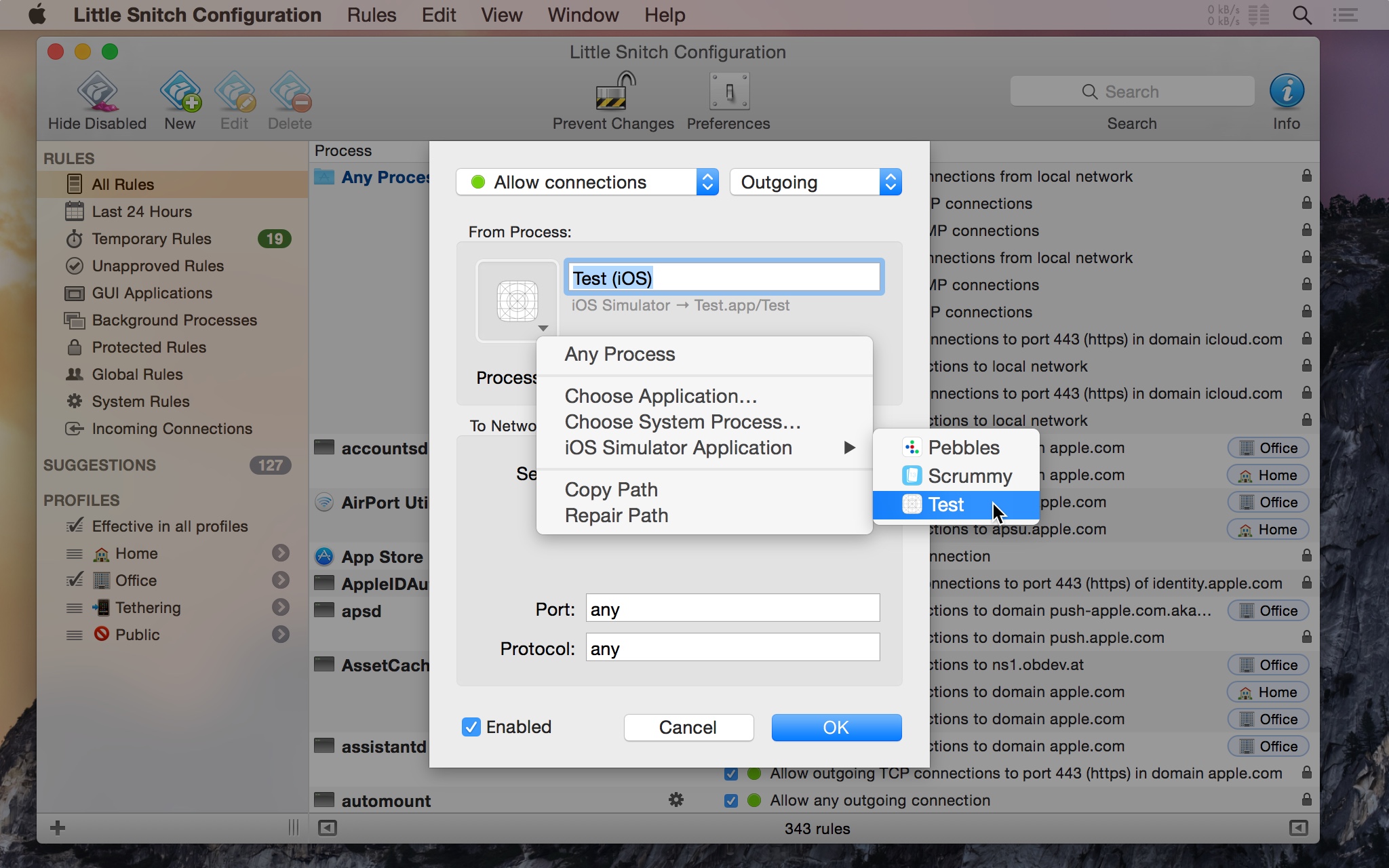
As a bonus, when creating a new rule in Little Snitch Configuration you get a list of all the apps that are currently installed in any of your iOS Simulator configurations, allowing you to create rules very easily:
Despite adding all of these improvements to Little Snitch, we made sure this convenience doesn’t open up any security holes whereby a malicious app could trick Little Snitch into allowing network access by just moving itself into an iOS Simulator container directory.
You can download the latest version of Little Snitch – including the latest nightly build that contains all this iOS goodness – on our Little Snitch download page.